In this article, we’ll learn more about this common condition.
Contents
I. What is Asthma?
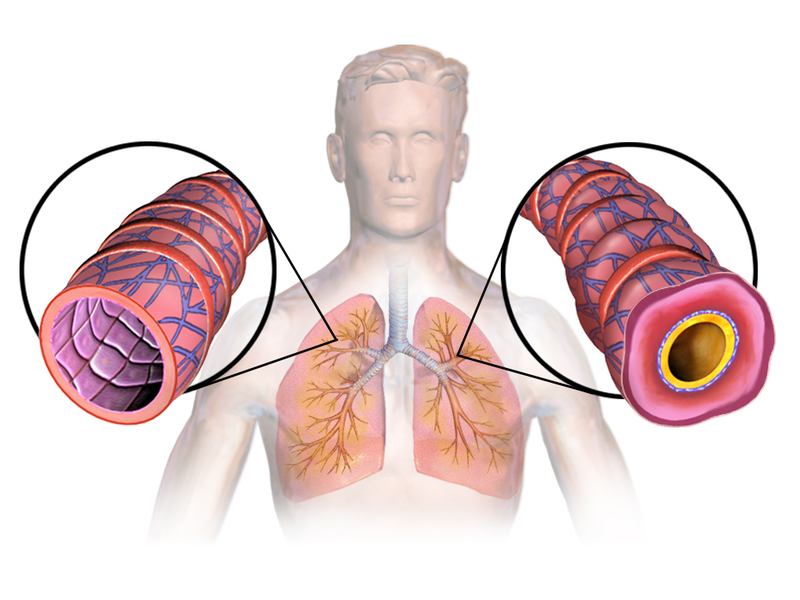
Asthma is a condition that affects the airways that carry air to and from the lungs. A person with asthma, also termed as asthmatic person if the condition is long-lasting or chronic, has airways that are inflamed or swollen. Due to this, the airways are sensitive to irritants. This is also the reason why asthmatic persons are more prone to allergies.
Because the inflammation causes the airways to become narrower, there would be less air passing through, less than what the body needs. This is the reason why the patient experiences breathing difficulties.
Sometimes, sticky mucus or phlegm builds up in the airways, leading to further narrowing.
II. Symptoms
The most common symptoms of asthma are the following:
- Chest tightness
- Coughing
- Breathing problems
- Wheezing
While wheezing is among the sure signs that a patient has asthma, not all patients actually experience wheezing. In fact, there are a lot of cases wherein the patient simply develops persistent coughing without developing or showing signs of wheezing.
III. Risk Factors
Millions of people around the world are suffering from asthma. According to Asthma UK, around 1 in every 11 children and 1 in every 12 adults are suffering from asthma. Of this, around 5% of the world’s population is suffering from severe asthma.
Surprisingly, while the condition affects more boys than girls, the statistics reverse in adults as more women are suffer from asthma compared with men.
Because asthma tends to be genetic, people who have parents or near relatives who have asthma tend to also have asthma or have the tendency to develop the condition.
The condition is also fairly common in families that have a history of allergies.
Smokers or persons living with smokers also have a higher risk of developing asthma.
IV. Causes
While most cases of asthma are genetic, it is actually possible for some forms of allergies to evolve into asthma or airway allergy, The Hindu states.
There’s also this thing called ‘occupational asthma’ wherein substances present in the workplace causes the airways to become inflamed, causing narrowing that leads to symptoms typically experienced by patients with asthma, reports Medline Plus.
Workers at risk of developing occupational asthma include:
- Laboratory workers (especially those working with laboratory animals)
- Plastics workers
- Metal workers
- Bakers
- Detergent manufacturers
- Drug manufacturers
- Grain elevator workers
- Woodworkers
- Farmers
- Millers
V. Diagnosis
Most doctors can easily diagnose asthma but because the symptoms can sometimes overlap with other conditions, many hospitals and clinics implement asthma screening. The test is simple and just lasts for about 15 minutes.
According to The American College of Allergy, Asthma & Immunology, the patient (or parents/guardians) will have to provide the doctor with basic information as well as family and/or medical history.
Then, the patient is asked to take a breathing test which simply involves blowing very hard into a special tube connected to a computer. This test will measure how well the patient’s lungs are functioning.
VI. Wrong Diagnosis
Just like other conditions, it is possible for a patient to suffer wrong diagnosis. According to The Hindu, there have been a lot of cases when the child who has asthma is diagnosed with primary complex, leading to an unnecessary regimen of anti-TB medications from 6 months to 1 year.
In such cases, the child is not cured of the condition because he does not have primary complex. Not only are the medications wasted, the child’s body was also forced to process the TB drugs when it has no need for these.
There are also times when the condition is mistaken for allergies.
VII. Treatment
While asthma is incurable, there are many ways to manage the condition, reports Medical News Today. However, patients need to consult a doctor to ensure that they are getting the right type of medications to address the symptoms they are experiencing.
Possible ways to manage asthma include the following:
- Use of nebulizer which delivers inhalation aerosol known as bronchodilators
- Use of inhalers
- Quick acting metered-dose
- Metered dose inhalers with spacers
- Breath-activated inhalers or dry powder inhalers
- Avoiding irritants and triggers
- Living a healthy lifestyle
VIII. What Happens to Patient Not Treated for Asthma?
While there is no cure for asthma, it is important for the symptoms to be managed to prevent the condition from worsening. Within two to three years of a child being untreated, he could develop what doctors call ‘airway remodelling’ which is actually an irreversible decline in lung function.
According to The Hindu, childhood asthma that is left untreated could lead to what is called as a ‘minimal persistent inflammation’. In this particular condition, the patient experiences airway inflammation but does not show any symptoms or outward signs of trouble.
When this happens, the child could have permanently damaged lungs which might not respond to aggressive treatments in the future.
IX. Is Asthma a Serious Condition?
While the condition is quite common and often manageable, it is actually possible to die of asthma. After all, the condition affects the airways which could lead a person to stop breathing if the inflammation causes blockage!
According to Asthma UK, it is estimated that 3 people die of asthma every day. Research shows that most of these deaths could have been prevented, if only these patients were given the right treatment or were able to follow their treatment plans correctly.
X. Prognosis
Surprisingly, despite the fact that the condition is not curable, prognosis is quite good for asthma patients. With proper management of their symptoms and using the right medications based on the severity of their condition, most patients with asthma live a long life and die of other causes, Medical News Today states.
Patients are able to get on with their lives as normally as possible; although they might have to bring along back-up treatments, such as inhalers, so they can enjoy strenuous activities or visit places that might trigger an asthma attack.





